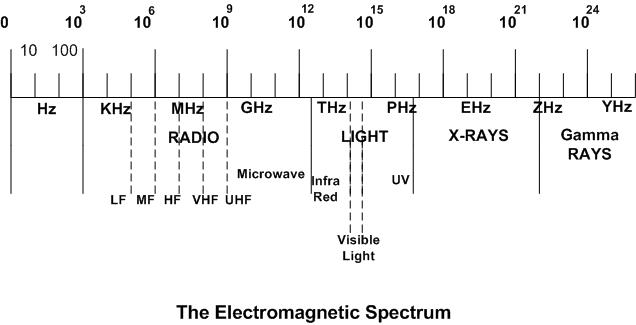
|
The origin of laser is based on Albert Einstein's research in the area of
thermodynamics (spontaneous emission and stimulated emission) and
"Stimulated Emission of Radiation" in 1917. In 1958, Charles Townes and
Arthur L. Schawlow, two physicists published a paper on laser theory that
led to the creation of a laser device by Dr. Theodore Maiman in 1960.
|
| |
|
The Theoretical Background of Laser
|
|
When a charged particle such as electron loses energy (by dropping) from
higher energy state to lower energy state,
EMR is emitted. The
emission of radiation can also be simulated (forced) by altering the
vibrational or rotational state of a molecule.
|
| |
|
By the theory of quantum mechanics, light is made of small particles
- photons. The fundamental equation that relates energy (E) of a photon
and frequency (ν) is as shown below
|
| E = ν x h
[1]
|
| h - Planck's constant (known
as Planck–Einstein relation) |
| |
| Other well know equation that relates velocity/speed (c),
frequency (ν) and wavelength (λ) is
|
| velocity = frequency x wavelength
|
| c = ν x λ
[2]
|
| |
| From equation [2], the frequency (ν) can be expressed as velocity/wavelength,
|
| ν = c / λ
|
| |
| By substituting the value of frequency (ν) in the equation [1],
it can expressed as
|
| E = c / λ x h = (c x h) / λ
[3]
|
| |
| With laser being related light, the following are the well
known constants
|
| Velocity of light c = 299,792,458 m/s (186,212 miles/second) |
| Planck's constant h = 6.626070 x 10-34 J-s (SI Units) |
| |
| By varying the wavelength value λ in equation [3],
the photon energy E emitted can be varied,
since c and h are constants. Thus intensity of laser
can be manipulated by varying the wavelength.
|
| |
| Top |